
According to the NHS, everyone should take a vitamin D supplement in the autumn and winter to keep bones, teeth, muscles, and the immune system healthy.
That’s because we here in the UK don’t get enough sunshine for half the year – meaning our bodies can’t make the vitamin D we need.
There’s a reason this super helpful vitamin is known as the ‘sunshine nutrient,’ and there’s a reason why it’s so important.
Join us as we explore the science behind vitamin D and discuss its health benefits. We’ll also show you how to make sure you’re getting enough.
Why is Vitamin D So Important?
Vitamin D helps our bodies absorb calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are crucial for healthy bones but consuming all the calcium or phosphorus you can get your hands on, won’t mean much without the vitamin D to absorb it.
Vitamin D does more than just support bones, however. It also boosts our immune system, improves mood, supports brain health and may even lower the risk of chronic diseases. Read on to find out more.
Understanding Vitamin D: The Fundamental Guide
So how exactly is vitamin D made and how does it function in the body?
Simply put, our bodies make vitamin D when we’re in the sun. The sun’s UV rays start a cellular reaction which turns into vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol. The body self regulates its production of vitamin D, so you won’t make too much.
How Much Sun Do You Need to Gain Enough Vitamin D?
 While varied factors influence how much sun people need – different skin types, location, season, environment etc… – on average you should aim for about 10-15 minutes of unprotected sun exposure per day. In the UK, the best time for this is between 11am-3pm in the spring and summer months.
While varied factors influence how much sun people need – different skin types, location, season, environment etc… – on average you should aim for about 10-15 minutes of unprotected sun exposure per day. In the UK, the best time for this is between 11am-3pm in the spring and summer months.
Note that if you wear sunscreen, your body will not make vitamin D. But you should be careful not to burn.
Different Forms of Vitamin D
There’s also a different form of vitamin D, known as vitamin D2 or ergocalciferol, which comes from plants but it’s the D3 version that raises blood levels of vitamin D most effectively.
Sources of Vitamin D3
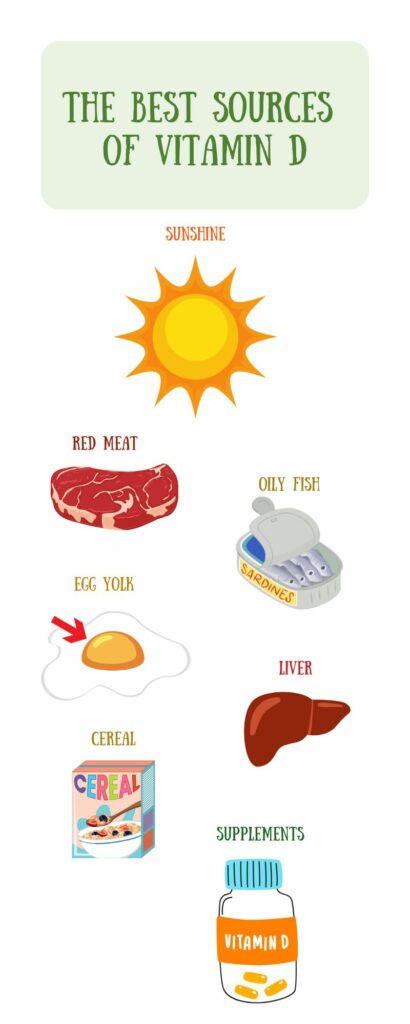 Everyone recognises that sunshine is the best source of vitamin D3, but you can also find it in a small number of foods such as:
Everyone recognises that sunshine is the best source of vitamin D3, but you can also find it in a small number of foods such as:
- Red meat
- Oily fish (herring, mackerel, salmon, sardines)
- Egg yolks
- Liver
- Fortified foods (some breakfast cereals, for instance).
Note that cow’s milk isn’t typically fortified with vitamin D in the UK as it is in some other countries, so this is not a reliable source of the vitamin.
There are also some quality vitamin D3 supplements available to top you up over the winter and autumn months, as per NHS advice. We’ll share our recommendations below.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
The NHS says people need 10 micrograms (10mcg) of vitamin D daily – that translates to 400IU or International Units.
It also recommends supplementing with a decent vitamin D supplement during October to March when there isn’t as much sun, as it’s difficult to gain enough of the vitamin from food alone.
In addition, anyone with little sun exposure (not often outdoors or you cover your skin when outside) – or anyone who has darker skin that may not make as much vitamin D – may want to supplement all year round.
Vitamin D’s Role in the Human Body
Let’s look in more detail at some of the jobs that vitamin D does in the body…
The Link Between Vitamin D and Bone Health
Vitamin D is key for strong bones and preventing osteoporosis. It helps the body absorb calcium from food, which is vital for bone health. Without it, bones can weaken, leading to osteoporosis. Getting enough vitamin D, therefore, helps to maintain bone density and structure while also supporting the formation of new bone tissue.
Boosting the Immune System with Vitamin D
Vitamin D is key for a strong immune system. It helps both the innate and adaptive immune responses work well. Having enough vitamin D and immune system levels can help fight off infections and diseases.
A joint study by the Universities of Surrey and Brighton found evidence that vitamin D3 could help the immune system fight against bacterial and viral diseases.
The study’s lead author, Professor Colin Smith, said: “We have shown that vitamin D3 appears to stimulate the type I interferon signalling system in the body – a key part of the immune system that provides a first line of defence against bacteria and viruses. Thus, a healthy vitamin D3 status may help prevent viruses and bacteria from gaining a foothold in the body.
“Our study suggests that it is important that people take a vitamin D3 supplement, or suitably fortified foods, especially in the winter months.”
The same study also showed that vitamin D2, the type of vitamin D found in plants, did not have the same benefits.
On the other hand, vitamin D deficiency makes us more likely to get sick and increases the risk of diseases like multiple sclerosis.
Keepingvitamin D and immune system levels up can therefore help protect us from illness and disease.
Mental Health and Vitamin D: Understanding the Connection
 Research shows a strong link between vitamin D and mental health. Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” it’s key for our mood and brain health. This section looks at how vitamin D and mental health connect, focusing on depression, SAD, and brain health.
Research shows a strong link between vitamin D and mental health. Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” it’s key for our mood and brain health. This section looks at how vitamin D and mental health connect, focusing on depression, SAD, and brain health.
Depression and Seasonal Affective Disorder
People with depression or SAD often have low vitamin D levels. Vitamin D helps make neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are vital for mood.
Taking vitamin D supplements may help ease depression symptoms and boost mental health. The NHS recommends it as one way to get through the ‘winter blues’.
Cognitive Function and Brain Health
Vitamin D is also linked to better cognitive function and brain health. The brain has vitamin D receptors, showing its role in brain processes. Research suggests vitamin D helps protect against brain decline, improves memory, and supports brain function. Research on mice, for instance, shows that a change in vitamin D in the diet (with no other changes) can influence the brain in as little as 20 weeks.
Researchers believe a vitamin D deficiency can accelerate age-related cognitive decline.
Mood Regulation and Emotional Well-being
Vitamin D also affects our mood and emotional state. Low vitamin D levels are linked to anxiety and mood disorders. Keeping vitamin D levels right can help maintain emotional balance and improve mental health.
- If you suffer from depression or any other mental health issue, please seek professional help from your doctor.
Vitamin D’s Role in Skin Health
Vitamin D is known for its benefits to bones and immune health. But its role in skin health and sports performance is also important. It helps keep skin cells healthy and regenerates them, making it key for glowing skin.
Vitamin D and Athletic Performance
For athletes, vitamin D’s effects on muscles are interesting. Vitamin D helps muscles grow and repair. This can prevent injuries and speed up recovery after exercise. It might also boost sports performance by improving heart function and reducing inflammation.
Vitamin D Deficiency: Signs, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Vitamin D deficiency is a common health issue. It can cause fatigue, muscle weakness, and bone pain. Even depression can be a sign. It’s important to know the risk factors.
Not getting enough sun is a significant risk. People who stay indoors or live in dark places are more at risk. Some health issues, like gut problems, also make it hard to use vitamin D.
Some groups are more likely to have vitamin D deficiency. This includes older people, those with darker skin, and vegans or vegetarians. Pregnant women and young kids are also at risk. They need regular checks and supplements.
Knowing the signs and risks of vitamin D deficiency helps. It lets people take steps to keep their vitamin D levels right. This supports their health and well-being.
How to Supplement Vitamin D Safely
Supplements can help if you don’t get enough vitamin D from food. Choose vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) for better absorption. Don’t take more than 4,000 IU a day without a doctor’s advice. Make sure not to take more than one supplement containing vitamin D – if you take a daily multivitamin, for instance, check that it doesn’t have vitamin D before taking a standalone supplement.
OUR RECOMMENDATION:
 Best Vitamin D Supplement: Performance Lab D3 + K2.
Best Vitamin D Supplement: Performance Lab D3 + K2.
Performance Lab’s combination supplement combines the might of vitamin D3 with little-known – but important – vitamin K2. K2 helps to direct calcium to the bones, while the D3 ensures your body can use it. K2 prevents calcium from accumulating in the blood vessels, so it also helps to protect cardiovascular health.
The two vitamins work exceedingly well together. The Performance Lab brand is known for its superior quality and clean products, and is a trusted manufacturer.
Read our indepth review of D3 + K2
- If you’re on any medication, please speak to your doctor before taking vitamin D supplements.