It seems that practically every bodybuilder or athlete is adding more protein to their diet nowadays, often in the form of pre or post-workout shakes. PhD Nutrition Recovery 2:1 fits into this market perfectly.
It seems that practically every bodybuilder or athlete is adding more protein to their diet nowadays, often in the form of pre or post-workout shakes. PhD Nutrition Recovery 2:1 fits into this market perfectly.
It’s not always easy to source enough protein from food, particularly if you have a busy lifestyle, which is where a workout shake comes in.
Why do you need protein after a workout? Simply put, protein is used in muscle production, as well as numerous other bodily functions, such as the creation of hormones, enzymes, the immune-system, and more. Protein is involved in pretty much every single cell and organ in the body, but it is its ability to help muscles heal that we’re particularly interested in here. Intense training causes micro tears to the muscles, tiny tears caused by contraction of muscles. Protein, once delivered to the muscles, starts to aid repair and recovery.
If the muscles don’t heal adequately and fast, it puts future training in jeopardy or puts you at risk for an injury caused by overtraining.
Solid food can take some time to break down protein, but a protein shake allows protein to reach the muscles as quickly as 30 minutes later. As your body naturally starts to heal muscle right after a workout, a quick shake is a good idea, followed ideally by a high protein meal an hour later.
Protein isn’t the only good idea after a workout – you need some carbs too.
You’ve no doubt heard the mantra urging you to choose Low Glycaemic carbohydrates over simple carbs to avoid insulin spikes and provide energy steadily throughout the day (to avoid the crash and burn method). Well, forget about that when it comes to post-workout. Post workout is one time where you should definitely opt for some simple carbohydrates to kick-start the whole recovery process.
During intense training, the muscles use both glucose and glycogen for energy, often until blood glucose levels get so low that there just isn’t any more energy to use. At that point, the body secretes cortisol, the ‘stress hormone’ which seeks to convert muscle tissue to glucose. This causes a loss of muscle tissue, something you want to rectify as soon as possible.
The quickest way to do this is to have a post-workout shake containing generous amounts of simple and High Glycaemic carbs which allows an insulin spike and supplies the muscles with nutrients.
The best ratio of Protein to Carbs is at least 2:1, with twice as many carbs as protein, though some studies and experts suggest ratios as high as 4:1.
PhD Recovery 2:1 provides 24g protein to 48g carbs. This is likely to be the ideal amount for anyone wanting to cut – i.e., to lose fat and build lean muscle at the same time, rather than anyone seeking a mass muscle gain.
The Ingredients
Protein: Whey Protein Isolate, Concentrate and Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate
PhD’s Protein Blend contains:
Whey Protein Isolate (Milk) (13%)
Whey Protein Concentrate (Milk)
Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate (Milk)
Whey protein is a popular protein form as it can be absorbed by the body much quicker than other protein alternatives such as milk protein or casein. Once it is absorbed, it promotes protein synthesis which in turn aids recovery and promotes muscle growth.
Whey Protein Isolate is a premium form of whey protein and generally comprises approximately 90% or more of pure protein. It also usually has little fat, limited lactose and lower cholesterol. Whey protein helps to boost energy and provide a rich source of BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids which aid muscle growth. It also aids muscle recovery.
Whey Protein Concentrate, in the middle of the list, is the cheaper more affordable form of whey, though it can still do a good job.
Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate is an even faster acting form of Whey Protein Isolate, broken down to be easier on your digestive system and boost speedy recovery. According to Men’s Fitness, hydrolysed whey digests in less than 30 minutes, which is what really makes this protein stand out from the rest. It’s just a shame that Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate comes at the bottom of the above list, meaning it comprises the smallest amount of protein included.
All in all, while it would be ideal for the protein in PhD’s Recovery 2:1 to be solely made from Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate, the combination of different whey protein forms still makes for a decent and effective protein source.
Note, however, that its leucine count is very low at just 0.48g (Men’s Health recommends a protein product with at least 3g of leucine), though PhD places its emphasis instead on Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate (4g per serving).
Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine Monohydrate is another popular pre and post-workout option, thought to boost strength, performance and aid muscle gains. There is some debate over whether taking it before or after a workout is best, but most people opt for the later. Four grams per serving may be a little on the low side, however (5g is considered optimal for maintenance) but studies do show that it works more effectively (up to 36% more so) when combined with simple carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates
The other important aspect to the 2:1 ratio, PhD Recovery 2:1 contains 48g of carbs. These are in the form of:
Maltodextrin (18%)
Dextrose Monohydrate (18%),
Waxy Maize Starch (16%),
Waxy Barley Flour (10%)
As we know, carbohydrates are an important part of a post-workout drink and the forms included in PhD Recovery 2:1 are pretty optimal.
Maltodextrin, while actually a complex carb made from potato starch, corn or rice, acts very similar to a simple carb thanks to its shorter molecular chain. Absorbed directly through the gut, it raises insulin and blood sugar levels without the dramatic drop that simple carbs can cause, offering a more sustained recovery.
Dextrose is also known as glucose and is a monosaccharide, meaning it is comprised of a single sugar molecule. It’s a more common sugar often used in post-workout shakes and boosts insulin and blood sugar effectively. Some people do find that the use of dextrose can result in fat gain, however, so you would need to test this product and assess its results. The good news is that Maltodextrin shows no apparent weight gain issues.
Waxy Maize Starch is the relatively new carbohydrate product on the block. It comes from corn starch and passes through the gastric lining to be absorbed super quickly, without any need for gastric emptying. It should also allow the Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate to be absorbed more speedily. The jury is out on whether it does actually create a rapid insulin spike, however, but it is potentially a useful carbohydrate to use in a stack. See some of the myths and realities of Waxy Maize Starch
Waxy Barley Flour is another carb but relatively little is known about this, compared to the more standard maltodextrin and dextrose. Quite what benefit it has over Waxy Maize Starch is unclear.
Added to the PhD Recovery 2:1 mix is 200mg of Vitamin C per 80g serving (two scoops), which is believed to help reduce tiredness and fatigue, and maintain the immune system during intense exercise.
Full ingredients list: Double Chocolate Flavour:
PhD Carbohydrate blend (Maltodextrin (18%), Dextrose Monohydrate (18%), Waxy Maize Starch (16%), Waxy Barley Flour (10%)), PhD Protein Blend (Whey Protein Isolate (Milk) (13%), Whey Protein Concentrate (Milk), Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate (Milk)), Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate, Reduced fat Cocoa Powder, L-Glutamine, Flavourings, L-Leucine, L-Isoleucine, L-Valine, Vitamin C, Magnesium Oxide, Potassium Chloride, Stabilisers (Guar Gum, Xanthan Gum), Sweetener (Sucralose).
The Pros
- The 2:1 ratio of carbs to protein is ideal for athletes or bodybuilders wanting to lose fat but maintain and build lean muscle mass.
- Contains enough good quality carbs and protein to aid with muscle recovery and potentially growth.
- Its mix of quick and slow acting carbs offers a quick and sustained recovery.
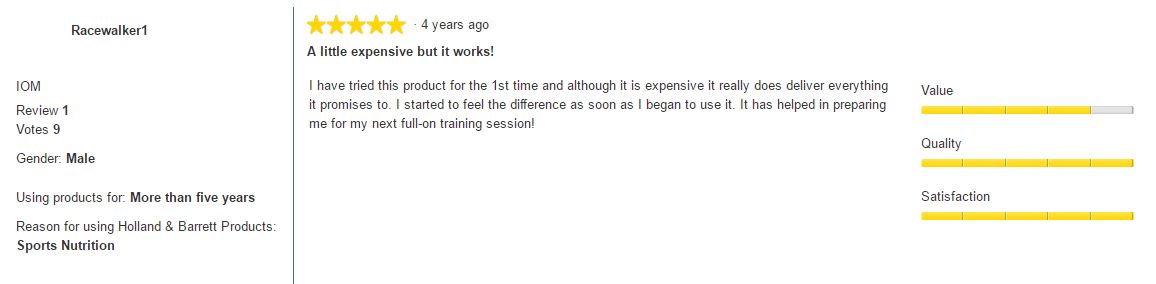
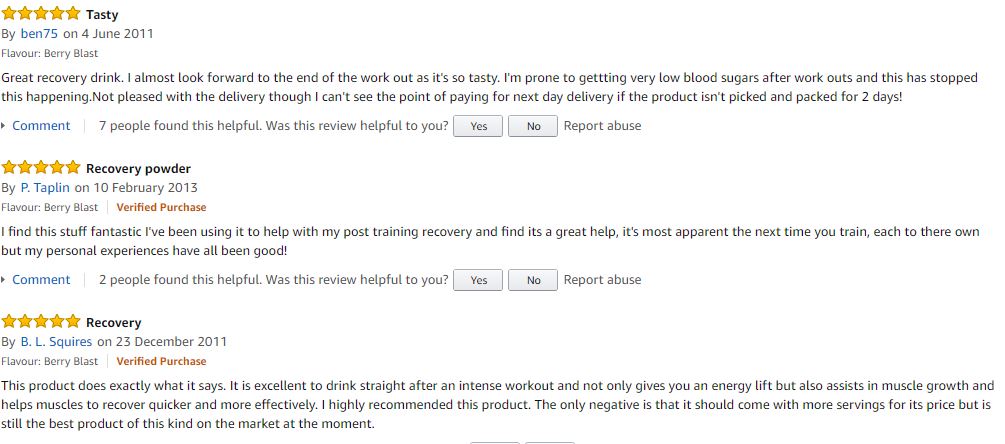
- The Berry Blast flavour has a 3.8 out of 5 star rating on Amazon UK
- Most people leaving reviews do say that it works to give an energy lift and aid muscle recovery so they are more eager (and able) to train again the next day. One reviewer even says they struggled to walk for three days after an intense exercise session when they didn’t take PhD Recovery 2:1.
- The mix of carbs in the product should ensure a rapid absorption.
- Vitamin C has been shown to help against oxidative stress, while magnesium supports muscle function.
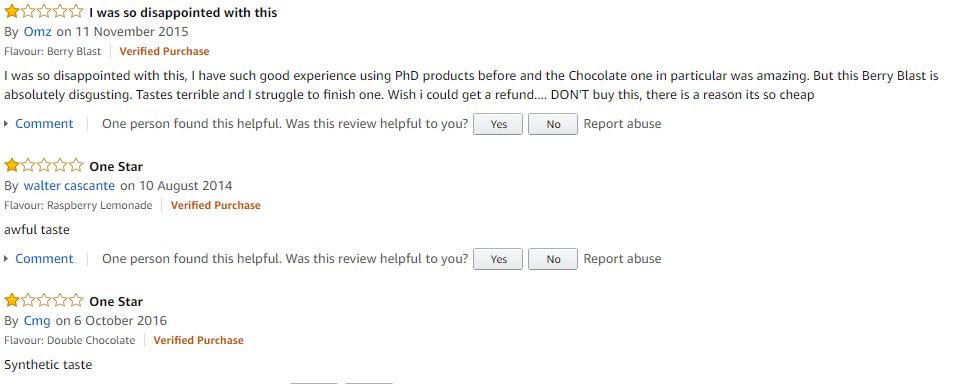
The Cons
- Slightly more expensive than competitor products
- It’s a shame its L-Leucine count isn’t higher.
- PhD Nutrition Recovery 2:1 stresses its additional L-Glutamine as a bonus, though it contains just 3.6g compared to the likes of LA Muscle’s LA Whey Gold which contains a much higher 10.7g. That said, Examine.com claims that there is no proven evidence that L-Glutamine aids recovery on anyone other than those with traumatic injury or muscle wasting disease.
Customer Reviews
The following review is from Holland ands Barrett
The following reviews are from Amazon UK for Berry Blast
Who Takes It?
PhD Nutrition states that Recovery 2:1 is suitable for endurance athletes who need more carbs, athletes looking to recover after intense exercise or athletes who require a high protein shake to boost muscles.
Safety/ Side Effects
There are usually few side effects with post-workout supplements, but some people may suffer from lactose intolerance. This is less likely with Whey Protein Isolate. Flatulence and stomach issues may also be a risk, as can nausea if you drink your shake too fast after a workout (leave it ten minutes).
Note too that the Department of Health recommends people avoid consuming more than twice the daily recommended amount of protein (55.5g for men and 45g for women) due to longer term concerns with osteoporosis and kidney issues.
How to Take It
Add two scoops of PhD Recovery 2:1 (80g) to 400ml of ice cold water and shake (in a PhD shaker cup) for ten seconds. Drink one shake daily, ideally within 10 minutes of completing intense exercise, according to the manufacturer.
Conclusion
PhD Nutrition Recovery 2:1 contains quality ingredients in mostly sufficient doses that should ensure you are provided with enough carbs and protein to recover after intense workouts. Its use of whey protein demonstrates its commitment to quality, while its fast and slow-release carbohydrates should help with both immediate and sustained recovery. Magnesium and vitamin C are also added to support muscle function and tackle free radicals that can cause damage to muscles and cells.
The majority of reviews of this product are positive.
It’s just a shame that its Leucine count isn’t higher as this is one of the branch-chain amino acids that really helps with muscle recovery.